Our quality measures illustrate how well we're doing and where we need to improve. To help you make an informed decision about your healthcare, we've provided our quality scores below.
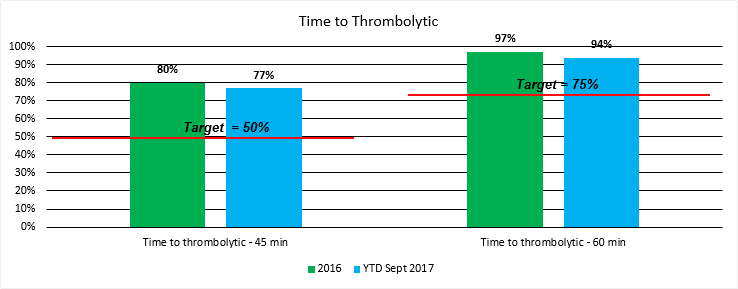
Time to Thrombolytic
When a stroke occurs, “time is brain.” In certain types of stroke caused by a clot, medications known as thrombolytics can be used to break up the clot and restore blood flow to the brain. These medications must be administered as quickly as possible. Receiving the drug timely greatly reduces the risk of permanent disability. The American Heart Association / American Stroke Association has set the goal for recognition of the highest performing hospitals to be 50% of patients receiving the drug within 45 minutes, and 75% of patients receiving the drug within 60 minutes. Mercy Hospital of Buffalo far exceeds these goals in both measures.
Interventional Procedures
Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive procedure performed to treat a brain aneurysm, which is a weakened area in the wall of an artery in the brain. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can cause bleeding, or hemorrhagic stroke. Our neurosurgeons at Mercy Hospital of Buffalo are specially trained to perform endovascular coiling. The procedure is performed during the angiogram. A catheter is inserted into a vessel over the hip and navigated through to the brain and into the aneurysm. Coils are then packed into the aneurysm, preventing blood flow from entering into the aneurysm. Over time, a clot will form, removing the risk of rupture or rebleed. As compared to surgical treatments, patients undergoing endovascular coiling generally experience shorter hospital stays, fewer complications, and quicker overall recovery times.
At Mercy Hospital of Buffalo, there have been no patients experiencing serious complications from an endovascular coiling procedure.
